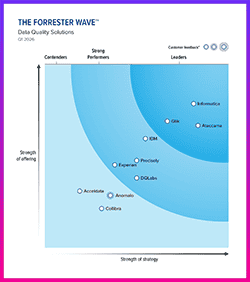
What is Data Governance?

And why is data governance important? Your success guide to all things data governance!
You can’t guarantee that your data will be accessible or reliable just because your company collects it. Enterprise data landscapes are incredibly complex, so it’s impossible to understand the state of data or work with data effectively without proper processes and tools.
Proper data governance is the solution to this. This ultimate guide will cover everything you need to know about data governance — the importance of data governance, best practices, data governance framework, pros and cons, and much more. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What is data governance?
First, let’s define data governance.
Data governance is a set of principles, policies, and processes established by an organization that ensures data availability, quality, and security for users within the organization.
Users are data consumers, and they are the main benefactors of data governance. These consumers can be humans (very often referred to as “the business”) or machines (think operational applications such as CRM, ERP, and external and internal APIs).
Usually, this is driven by the data governance office and executed by data stewards. These individuals will compile the rules and processes that govern how the company handles the organization’s data and make the information available to all relevant parties.
Why is data governance important? (5 Benefits)
Every organization dealing with a large amount of data without good data governance and management will face many problems. For example:
- Data scientists spend more than 80% of their time searching for data and cleansing it, and the rest building models.
- Business users complain to IT about poor data quality.
- BI (Business Intelligence) tools designed to be self-service fail at the point of understanding data by users.
- Regulatory reports are prepared in panic mode.
Quality data governance and management brings organizations numerous benefits, but the main ones we want to highlight include the following:
1. Enhanced data quality
Data quality is placed at the top of the priority list with a strong data governance framework established. Overall, it’s self-explanatory — data quality focuses on the quality of your data sources including relevance and accuracy.
More accurate and reliable data results in users having more trust and faith in the data collected within an organization. As a result, it leads to better business decision-making and fewer missed opportunities.
2. Faster data accessibility
Another key benefit of clear data governance and management is making necessary data more accessible to the right users in an organization. Data governance relies heavily on data cataloging, which delivers a single, searchable inventory of an organization’s data sources.
Getting accurate, consistent, and reliable data into the hands of necessary stakeholders as quickly as possible is a major benefit of data governance.
3. Trustworthy data results in cost savings
With enhanced data governance frameworks in place, an organization can save valuable time and money through:
- Improving the efficiency and effectiveness of internal operations.
- Enhanced data quality leads to wiser business decisions.
- Identifying bottlenecks, redundancies, and obsolete data.
- Faster accessibility to data saves time and productivity for team members.
4. Reduce risks & increase security
Data governance and management also increase the security and privacy of an organization’s or user’s data. These practices minimize risks and data breaches by upholding regulatory compliance measures.
This is yet another way an organization can see financial benefits because these enhanced security measures help avoid major penalties and financial losses.
5. Increase transparency within data sources
Data governance practices deliver transparency into an organization’s data through data lineage tracking. This means that users can follow along with a data set’s journey to see where any changes have occurred, allowing people to see the latest version of the data they’re working with.
What are the goals of data governance?
Data governance frameworks put the rules and processes in place to achieve several goals for your organization. Data consumers primarily care about data availability and data reliability. Let’s break these two down.

Data availability
- Speed of search: A data user should be able to find the data they need, verify it is indeed the data they were looking for, and start using it. Users should also have a good idea about what is available in general.
- Metadata management: Understanding the meaning of data, different and similar business terms, and calculated values. A data user should be able to browse related metadata objects and view data lineage.
Data reliability (AKA trust in data)
- Data authenticity: Understanding the origin and quality of a specific data set.
- Data quality transparency: Understanding what enterprise data can be used for a specific purpose at hand.
What are the 4 data governance pillars?
Now that we know the goals of data governance, let’s discuss data governance pillars and how they’re necessary to achieve these goals.
The data governance office manages these and some other components in conjunction with other departments, such as IT, Legal, Compliance, or Security. For this article, however, we’d like to focus on the components of data governance that no other function or department usually initiates or is interested in. These components are:
- Data stewardship
- Data quality
- Master & reference data management
- Metadata management
These four directly cater to data consumers’ needs by creating policies and processes that ensure data is available and of high quality continuously.
Data stewardship
The data steward is the person responsible for an organization’s data. They’re a key data governance pillar because they help enforce strong data governance and management practices throughout the entire organization.
Data stewards collaborate with a variety of specialties as well, including data quality analysts, Business Intelligence professionals, database administrators, executive leadership, and many other roles that heavily rely on data.
Data quality
Another data governance pillar is data quality. It’s been mentioned numerous times throughout this ultimate guide already, indicating just how important this is to data governance. Data quality is about establishing processes and metrics to ensure that data is fit for processing and further use, such as analysis, reporting, BI, data science, etc. Data quality is a crucial component of data governance because it makes the state of data objectively measurable.
Your data governance program will help define metrics and processes for how your company ensures data quality. Inthe initial stages, the data governance office (represented by data stewards) will collaborate with different lines of business to understand the most common data issues and set up rules for data validation, cleansing, and monitoring. For example, if your company does not serve clients under 18, you can define that as a data quality rule in your data governance program.
Here is an example of a data quality monitoring project focused on PII (Personally Identifiable Information):

Based on the most common data use scenarios (like financial reporting), the data governance office will also help define thresholds for high and poor data quality. It will set up processes for proactive data quality, such as capturing issues early and automatically correcting them, assigning data stewards to more complicated matters, and educating users in general.
Master & reference data management
Master and reference data are both critical data types within any large organization. Both act as a single source of truth for various data consumers. Master data Management includes information about people, things, and locations. However, Master Reference Data Management is a set of codebooks for categorizing master and transactional data.
Data governance can help by developing rules and processes around managing master (MDM) and reference data (RDM). Master data governance can contain directions for forming the “golden record,” especially when data from different sources conflict.
In some cases, data stewards need to review a particular golden record and decide on specific attribute values:

Other important aspects of data governance include defining rules for who can create, change, and delete master data and business workflows for approving these changes. You can also define rules about who can access what master data and how it can be used.
With reference data (especially externally procured), data governance helps identify the processes and systems that consume the same (but often duplicated) reference data. It then strives to establish a centralized reference data management tool. This eliminates multiplied spending on the same reference data and simplifies the process of updating to newer versions of codesets when they need to be changed or become outdated.
When it comes to internally authored reference data, data governance and management set rules for approving changes, for example, via the four-eye principle and avoiding problems for data consumers.
Metadata management
Metadata management is about creating an enterprise-wide understanding of data to increase data availability and decrease “time to data.” Achieving these goals requires setting up data governance tools like a data catalog, a business glossary, and data lineage.
Here is an example of a listing of assets in a data catalog:
 Data assets listed in the data catalog
Data assets listed in the data catalog
The data governance office helps with setting up these tools, making them part of change management, and integrating them into vital data-related processes. It establishes procedures and provides the tools and methodology for filling in the data catalog and business glossary.
It is then up to specific business units and departments to create consistent definitions of essential business terms, document the calculation of various KPIs or metrics, and keep track of company policies. This way, they create a common point of reference for everyone.
It’s worth noting that modern data catalog software integrates with data quality tools to provide transparency about the state of any data set that users find in a data catalog or any business term they find in the business glossary.
In the example below, users can review the overall quality of personal data and drill down to see which systems and tables contain it:

What are the data governance program challenges?
Now, let’s cover some common data governance challenges to prepare you for all obstacles along the way:
- Limited resources: There are a lot of moving parts to implementing a data governance and management program. Without the proper resources, it could prolong the process or make it entirely impossible if the key stakeholders aren’t on board.
- Disorganized and inconsistent data: While this isn’t a complete obstacle (data governance seeks to rectify this issue), having your data spread out in a disorganized manner or being inconsistent can slow down the implementation of a data governance framework.
- Aligning key stakeholders: A significant challenge can be aligning stakeholders on what the key datasets and sources are, their respective definitions, formatting, and those necessary details. It’s best to have some plan in motion and to communicate effectively to keep everyone on the same page.
- Evolving Privacy Regulations: GDPR and CCPA are ever-changing, which can make implementing a data governance program challenging if rules are constantly evolving. You have control over your program rather than privacy regulations, so a data governance best practice is to ensure it’s adaptable.
4 data governance best practices to ensure a successful program launch
Not all data governance programs successfully launch or continue growing if they do. There are several data governance best practices to keep in mind before and during implementation. We will briefly cover them here.
1. Start with a business problem and solution
The first data governance best practice is having a business case. For example, instead of offering data governance with the goal of “having better data,” sell it to the business as a solution to a problem they have: ineffective data science or lack of self-service data discovery.
2. Secure funding and buy-In from upper management
Data governance is a complex end-to-end program that, upon its maturity, covers the entire organization and impacts many processes and systems. Therefore, after building the business case, it’s vital to secure funding and get buy-in from key stakeholders (CFO, COO, Head of IT, and others).
3. Start small but keep an organization-wide perspective
It’s wise to break down the data governance program into manageable steps and go one step at a time, solving practical issues and showing value at each stage. For example, you could start with improving the quality of data for an important regulatory report.
A vital data governance best practice is to set up roles and processes with the future perspective of data governance and management being an organization-wide program.
4. Communicate often
It’s essential to communicate the success of the data governance program along with the significant milestones of its implementation. Effective communication tools are product demos, dashboards with metrics, and presentations to executives.
Data governance FAQ
Here is some more information about data governance if you’re still curious.
1. What is master data Governance?
Master data governance focuses on the “master keys” within the data governance framework:
- Customer data
- Product data
- Employee data
The goal of master data governance is to ensure that the master keys listed above are accurate, complete, consistent, and secure.
2. What’s the difference between data management vs data governance?
The difference between data management vs data governance is slim – they both work to achieve the same thing. Their greatest difference lies in the nuances of their roles:
Data management focuses on the implementation whereas data governance is the set of rules and policies for how the data is to be managed.
3. What does a data governance framework look like?
A data governance framework is basically a toolbox with a set of instructions on how the data governance program should work. It’s made up of various components including:
- The mission statement
- Goals, metrics, and other focus areas
- Rules and definitions for data sources
- Policies
- Processes
- Technologies
- Structures
- User responsibilities
Various data governance frameworks available today can include up to 10 components of data governance. You will find that “The DAMA Wheel” links the concept to every corner of the data management spectrum, from data quality down to data storage. You’ll find things like data integration, data architecture, data modeling, data security, and others.
The data governance office manages these and some other components in conjunction with other departments, such as IT, Legal, Compliance, or Security.
4. When do you need to implement a data governance plan?
If your company is collecting a relatively small amount of data, you probably won’t need a data governance framework, or at least not a very complex or stratified one.
As companies grow larger and their data systems more complex, they need to put these rules and processes in place to ensure their data remains useful and of high quality.
You might also need data governance programs if a new law or data regulation goes into effect. This way, you can know the type of data you’re storing, how sensitive it is, and who has access to it.
You might also need data governance to align with existing regulations like the GDPR or the California Consumer Privacy Act.
5. Who is responsible for data governance?
Executing a data governance framework effectively requires the collaboration of three parties:
- IT
- The business
- Data governance office or data governance committee

IT owns technologies, creates simple technical checks, ensures technical processes work (such as ETL), and monitors changes in data structures. At the same time, IT lacks the end-to-end understanding of business processes and looks at data from a purely technical perspective.
The business understands the meaning of data. They are instrumental in creating checks and business glossary content. In the end, they benefit the most from data governance. However, they have a view of data limited by their product or business process.
Finally, the data governance team looks at all enterprise data and owns methodologies and processes for effective management. This team’s approach to issues in data is proactive. However, they lack specific knowledge of business processes and systems or specific data.
The three teams help each other with their strengths and cover other teams’ weaknesses. Once the data governance framework is set in place, it’s primarily maintained and enforced by a data steward or a data custodian.
Time to invest in a data governance program
To summarize, data governance is a set of rules, policies, and processes put in place by a company to ensure data availability and reliability. While it can be linked to several components of any data strategy, its four key components are data stewardship, data quality, master data management, and metadata management.
Remember the following:
- It’s never too early to start a data governance plan.
- Data governance requires collaboration between the business, the data governance team, and IT.
- Data stewards are pivotal to executing a data governance initiative.
- The success of data governance requires approaching it with the right mindset, getting buy-in, and executing it correctly.
- Software alone will not cure your data troubles, but data governance tools are an important technological component.
Utilizing data without proper governance is close to impossible. If your business has a lot of source systems and data types, then it’s only a matter of time before you realize you cannot trust your data.
Some data governance programs fail because of unintuitive tools. Here at Ataccama, our goal is to help organizations implement a strong framework with our modern data catalog software. We achieve this by building easy-to-use user interfaces and automating tedious, time-consuming tasks.
Interested in learning more? Contact our team for more details or to schedule a demo!