Data quality analyst careers: Essential skills to stand out in the industry

The idea of data quality seems straightforward, but having data and having good data are two separate things. Data quality encompasses maintaining and cleaning large data sets across an organization’s entire data chain. Ensuring data quality requires consistent monitoring, keeping the data accurate, reliable, and usable at all levels of the organization.
In our data-driven world, high-quality data is one of the most valuable assets for any company. If that data is incomplete, inaccurate, or stale, an organization risks making decisions and implementing strategies based on the wrong factors. That’s where data quality analysts come in.
What does a data quality analyst do?
A data quality analyst is responsible for maintaining the integrity of data from end-to-end across an organization. The work of a data quality analyst ensures that all data is reliable and well-managed, which enables teams at all levels of the company to make empowered business decisions.
Essential skills and competencies of a data quality analys
A great data quality analyst — sometimes called a data quality assurance analyst — possesses some essential skills to help them keep all this data in line. A combination of technical skills, analytical aptitude, and communication skills all work together to allow a data quality specialist to excel in their role.
Technical skills needed for success
The role of data quality analyst is a thoroughly technical one. The ideal data quality analyst is proficient in the following skills:
- Data quality tools
- Data cleaning techniques
- Database management
- Data profiling and SQL (Structured Query Language)
- Data analysis
- Data profiling
- Programming languages, such as SQL, Python, and R
- Data integration
- Data ETL tools (Extract, Transform, and Load)
- Data governance
- Master data management (MDM)
- Statistical analysis and data quality metrics
These technical skills are essential to performing the duties of a data quality analyst, in addition to communication skills and more.
Analytical and communication skills
Any data quality analyst job description will also require excellent analytical and communication skills. This role is responsible for maintaining the database, but also for troubleshooting errors when they arise, often across multiple software stacks or databases. Being able to think critically and make predictions that affect the process multiple steps downstream is essential to proficient data management.
Another skill necessary for a data quality analyst is to know when to escalate errors up the command chain when necessary to ensure that incorrect data is resolved in a timely fashion. If the c-suite doesn’t know about errors in time to make business-critical decisions, then the data quality analyst skills aren’t being used to their full potential.
Data quality analysts will also be expected to have excellent written and oral communication skills, and should be able to create and present reports to working groups and boards when necessary.
Tools & technologies used by data quality analysts
Data quality analysts use a variety of specialized data quality tools for their tasks. While being well-versed in programming languages and Microsoft Excel is a given, data analysts must also have familiarity or expertise in data-specific software.
These data-analyst specific tools include:
- Data manipulation and visualization tools, like Microsoft Excel or Tableau.
- ETL and data wrangling tools like IBM InfoSphere DataStage or DataLadder.
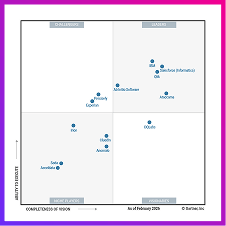
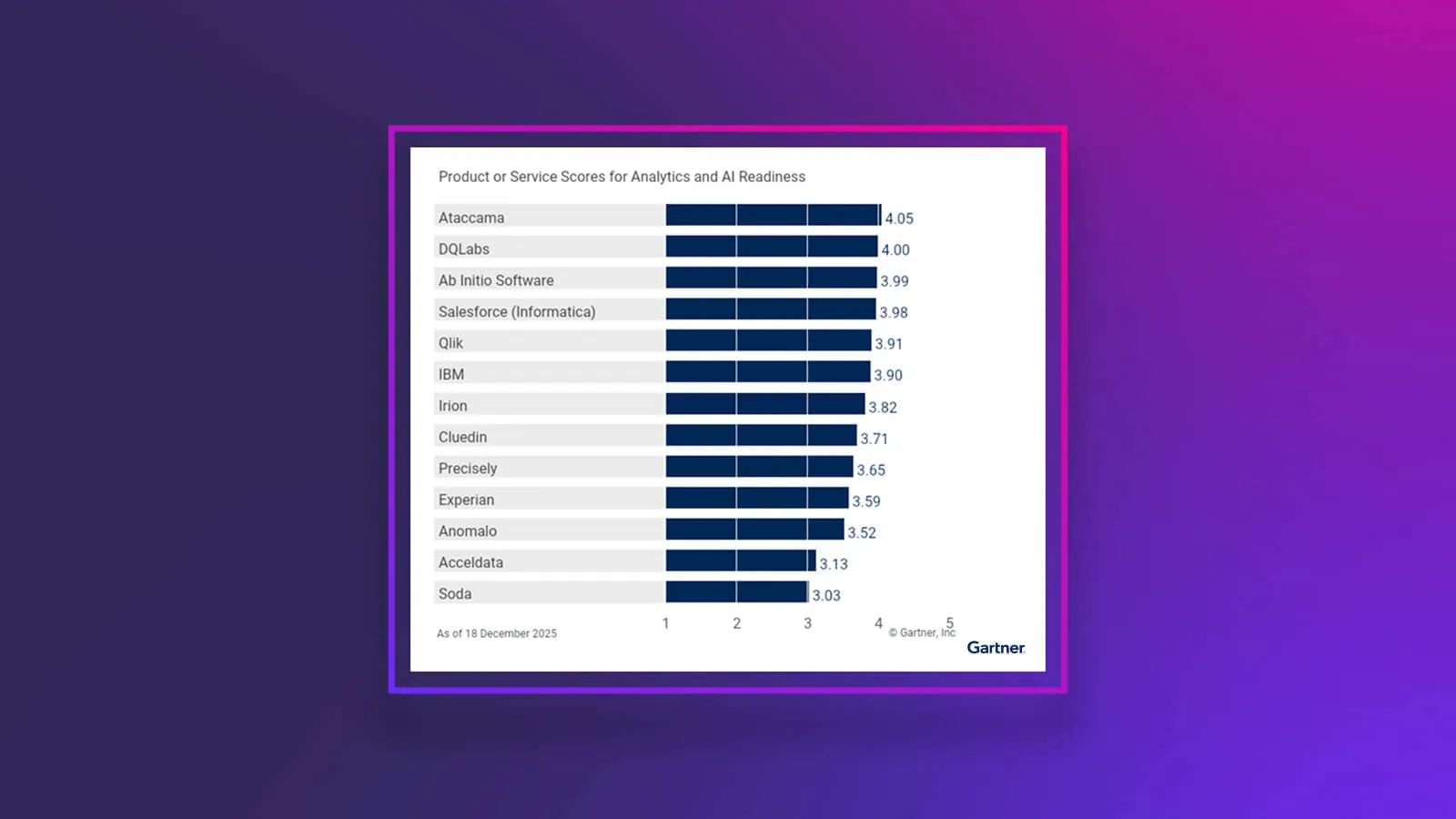
- Specialized software specifically created to manage data stacks, like Ataccama ONE, Informatica, and others.
The importance of data quality analysis for organizations
Why is data quality important for businesses? The world runs on data. If that data is incorrect, incomplete, or missing the necessary context, there can be operational, financial, and even legal consequences. A great data quality analyst provides a sort of in-house audit of an organization’s data, helping them to stay compliant, operate efficiently, and make big-impact decisions in real time.
When a data quality analyst is doing their job well, every team across an organization is empowered to operate with confidence. For example:
- Team leaders and c-suite executives can make strategic decisions, knowing they can be confident in the information they have at their disposal.
- Operations teams can create efficiencies and increase business values.
- Compliance teams can meet regulatory requirements with less effort.
- Sales teams and marketing groups can target the correct customers with the messages that will be most effective.
True growth in today’s economy can only happen when accurate data is accessible and usable for all levels of an organization.
Career path and salary expectations for data quality analysts
Individuals can expect to start with an entry-level data quality analyst position and work their way up to a senior data analyst or even a c-suite leadership position, like Chief Data Officer (CDO).
When entering the workforce, look for job descriptions with data analyst, data quality analyst, data engineer, and other related key words. Entry-level data analyst positions do exist, but developing a portfolio of work while in school or before entering the job market can help your application stand out among the rest.
A data quality analyst job description will often list a salary in the range of 50,000 to 65,000 for an entry-level position. More experienced candidates can expect to see 67,000 or more, and in advanced roles and/or roles in a high cost of living area, many data quality analysts can expect a salary of 75,000 or more, and on up to 100,000 and above.
How to become a data quality analyst: steps and education
Interested in becoming a data quality analyst? Earn a bachelor’s degree in a quantitative field, like computer science or data science. A master’s degree may also be required for more advanced or senior level data quality engineer positions.
In addition to a degree, data quality analysts can distinguish themselves in their field through earning industry-specific certifications. Becoming a Certified Data Management Professional (CMDP) is one such certification, and there are others available from specific companies like Google or Microsoft when you become proficient in their specific products.
Outside of formal education, many data analysts spend time developing technical skills that enhance their capabilities within their field. Learning a new skill, or becoming more proficient in skills like SQL, Python, R, and case-specific data quality tools all help to elevate an application for a data quality analyst position.
In addition to the technical aspects of the role, aspiring data quality analysts could benefit from courses in communication and public speaking, helping them to learn how to communicate effectively to both technical and non-technical roles.
As with every rapidly-changing profession, data quality analysts should expect to continue learning on the job as their tools and responsibilities evolve.
Key challenges faced by data quality analysts
There are many challenges that data quality analysts face in today’s data-driven world. As with many other fields, the world of data management is rapidly expanding as more and more data is generated and stored — and as companies try to make sense of all that data in a usable way.
A few specific data quality challenges include:
- Data silos and inconsistent data formats. As companies grow, they add on different software as needed to handle different parts of the business, not always thinking about how they will fit together in the long run. This means that many data sets are siloed off from each other, even within the same organization, and may not even be in the same format. Data quality analysts must be able to troubleshoot across software stacks and be able to make recommendations to avoid increasing data silos.
- Adapting to changing data requirements. The rapid pace of data growth means that regulation is often catching up to what is already loose in the world. Data analysts need to stay on top of changing regulations and make sure their organization is meeting the data requirements for their location and their industry.
- Managing high volumes of data. It can be dizzying to experience the high volume of data coming at an analyst in an organization. Being able to prioritize, troubleshoot, and make fast-paced decisions is essential to a data analyst.
Best practices for data quality management
Every data quality analyst should strive to establish best practices in their organization. This may take time, so starting with a high-impact solution first will create the most significant change, yielding a win for the data team and the organization.
Some data quality analyst best practices to consider:
- Establish data governance. Data governance is the framework for dealing with data in your organization, where a data and leadership team define clear policies, ownership roles, and specified data stewards who are responsible for all pieces of data quality. When established, good data governance can help to avoid fiascos in the future.
- Create a culture that values quality data. Good data isn’t just the job of the data team. Every corner of an organization must be committed to creating good data and stewarding that data through collaboration.
- Implement data quality management training. All members of an organization need to know the importance of keeping data safe, and the best practices to ensure protected information is handled responsibility in every instance.
- Self-audit regularly. Implementing automatic points where quality checks run and validation rules are verified help to improve data quality for the long haul. PULL QUOTE: Implementing a system like Ataccama ONE means that errors can be traced back to their source through root cause analysis, and resolved before they become an issue down the data pipeline.
Conclusion
Becoming a data quality analyst can be a rewarding endeavor. Not only does it provide an invaluable service to an organization, but it also combines a technical skillset with a love of troubleshooting, an ideal environment for someone who values analyzing and resolving problems in a fast-paced setting.
Frequently asked questions
- What does a data quality analyst do?
- A data quality analyst monitors an organization’s data, ensuring that the data is complete, correct, and up-to-date. They handle troubleshooting data errors, and provide leadership with the data details necessary for sound decision making.
- What skills are needed to become a data quality analyst?
- Data quality analysts need technical skills, like computer programming and database management, in addition to analytical skills, troubleshooting skills, and communication skills.
- Why is data quality important for businesses?
- Data quality is important for businesses because large amounts of data can become easily corrupted or corroded if they are not managed properly. Ensuring quality data across the entire organization empowers fact-based decision making at all levels, as well as helps to meet compliance and regulatory requirements.
- How does a data quality analyst differ from a data analyst?
- Though similar, the roles of data quality analyst and data analyst are distinct. A data analyst uses data available to pinpoint insights and inform decision-making, while a data quality analyst is more focused on the quality of the data, ensuring that it is accurate, reliable and complete.
- What tools do data quality analysts use?
- Data quality analysts use a range of tools, from Microsoft Excel to programming languages like SQL and Python, as well as specialized software that allows for data cleansing, root cause analysis, and more — software like Ataccama ONE.
- What are the main responsibilities of a data quality analyst?
- The main responsibilities of a data quality analyst are to maintain an accurate, reliable, and complete database for their organization, as well as troubleshoot errors and present findings to team leadership.
- How do data quality analysts improve data governance?
- Data quality analysts improve data governance by noticing patterns that lead to incorrect data, resolving root cause issues, and eliminating data siloes within an organization.
- What qualifications do you need to become a data quality analyst?
- To become a data quality analyst, you need a bachelor’s degree in a related field, such as data science or computer science, as well as relevant experience with programming languages and database software.
- How can data quality analysts help organizations reduce costs?
- Data quality analysts help organizations reduce costs by providing operations teams with the information needed to create operational efficiencies, as well identify pieces of the business that may or may not need investment or divestment.
- What are common challenges faced by data quality analysts?
- Data quality analysts face the common challenges of working with data siloes, incomplete data stacks, high volumes of data, changing data regulations, and organizations that don’t understand the value of their data.
David Lazar
David is the Head of Digital Marketing at Ataccama, bringing eight years of experience in the data industry, including his time at Instarea, a data monetization company within the Adastra Group. He holds an MSc. from the University of Glasgow and is passionate about technology and helping businesses unlock the full potential of their data.