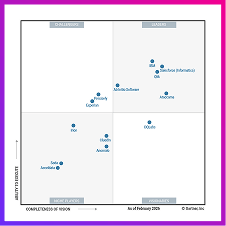
What is data lineage? A complete guide

As data moves through an organization, it’s possible to lose track of its origin, intended purpose, or even its final destination. You may have disparate data sources, several different data owners, or trouble finding who to go to when something goes wrong.
However, understanding precisely where data comes from, how it transforms, and its journey is essential to maximizing its value. That’s where data lineage comes in. It offers a clearer picture of your data landscape and its reliability.
This article will dive into what data lineage is, why it is important, best practices, and more.
What is data lineage?
Data lineage tracks data from its source to its final destination. With specialized data lineage tools and software, you can automatically map and visualize the entire lifecycle of your data assets.
What are the two types of data lineage?
There are two ways of doing data lineage, at the table-level and at the column-level (field-level)
Table-level
Table-level data lineage is the most basic and frequently used. It shows the relationships between different tables in a data environment. While it provides insight into how a particular table is constructed, it does not reveal the source of the data within that table.
Column-level (field-level)
Column-level data lineage, in contrast, serves as a detailed map tracking a data asset’s journey from the point of ingestion through to its final destination. This level of lineage is crucial in data observability, as it enables data engineers to swiftly identify the root cause of data quality issues and perform impact analysis to determine which downstream processes or systems may be affected.
A practical data lineage example here would be tracing an incorrect sales figure back through each transformation step until the original data source is identified.
5 common data lineage challenges
It is difficult to map and maintain data lineage across an organization. Here are five reasons why.
1. Complex data environments
Modern data environments can be very complex because of the volume and variety of data sources, transformations, and endpoints involved. All of this can complicate the data lineage mapping and visualization process. As a result, there can be inaccuracies and gaps in information.
2. Varying or unclear standards
Another data lineage challenge is when an organization has varying standards for how data lineage is represented across different systems. Lack of standardization can lead to inconsistencies and difficulties in integrating lineage information from multiple sources.
3. Large amounts of data to track
If an organization has a large volume of data to manage, it becomes incredibly difficult to rapidly process and maintain updated lineage mappings. High data throughput can complicate the task of tracking and documenting the flow of data.
4. Data that changes frequently
Data that is frequently modified can make the data lineage tracking process more difficult. Frequent changes in data structures, processes, and systems complicate data lineage mapping, requiring diligent maintenance and ongoing updates to successfully track the flow of data.
5. Inability to integrate with other systems
If a data lineage solution can not integrate with the systems an organization uses, it poses a major data lineage challenge. Compatibility issues and integration complexities can make tracking data more difficult or hinder your ability to do so altogether.
Why data lineage matters and the benefits it brings
Data lineage is all about knowing your data’s story. When you understand where data comes from, how it changes, and where it goes, you can trust it and use it with confidence. This makes your work smoother, helps you avoid mistakes, and ensures you get the most value out of your data.
Why it matters
- Trust: You can trace data issues back to their source and make sure data is reliable.
- Compliance: Regulations like GDPR and CCPA require clear proof of how data is handled. Lineage makes it easy to show that you are following the rules.
- No more silos: With a shared view of data, everyone from data engineers to business users and data stewards can work together instead of fixing the same issues in isolation.
- Smooth operations: By knowing how data connects across systems, you can make changes or migrate data without creating unexpected problems.
The benefits
- Better data governance: Data lineage supports effective data governance by providing a better understanding of data, so you can more accurately execute data policies and keep data secure.
- Faster troubleshooting: When something breaks, you can quickly see where the issue started and fix it without delay.
- Collaboration: Everyone from data engineers to business users gets the same context about data, so decisions can be made faster and more accurately.
- Confident changes: You can see the impact of a change before making it, which helps avoid surprises and allows you to plan as needed.
In short, data lineage builds trust in your data, helps teams work better together, and keeps your organization ready for whatever comes next.
What are the components of data lineage?
We’ve established what data lineage is and why it’s important. Now, let’s review its core components.
Imagine tracking a customer order from a CRM system, through a data warehouse, and finally into a BI dashboard. Each step of the way, data lineage shows where the data order is stored, how it is transformed, and how it is ultimately used. This kind of mapping makes it easier to understand the data’s full journey and trust it.
These data flows are often displayed in a data lineage diagram. This diagram provides a clear visual of the flow from source to destination, helping both technical and business users see how data moves across systems.
Components of a diagram include:
- Data origins/sources: Identify where your data comes from and the owner responsible for that data in databases, applications, third-party data feeds, etc.
- Data flows and transformations: Track every modification made to data (data transformation) and every destination it passed along its journey (calculations, aggregations, merging datasets, data quality improvements, who accessed the data, etc).
- Dependencies: Understand relationships between data elements and how they impact each other.
- Metadata insights. Include essential information that provides context about data assets, organizing them into technical categories and different business processes.
Top features to look for in a data lineage tool
When comparing different data lineage tools and platforms, it is important to focus on the features that make them practical for everyday use.
The right solution should not only track data flows but also simplify visualization, improve collaboration, and reduce manual work. Below are some of the most valuable features to look for.
Automation
Modern data lineage tools use automation to keep lineage accurate, comprehensive, and continuously updated. Using automated scanners, they connect to databases, ETL/ELT pipelines, BI platforms, and data lakes to harvest metadata and parse SQL and workflow logic to map data transformations at a granular level and generate interactive, end-to-end lineage diagrams without manual effort.
Look for tools that continuously detect changes, assess their downstream impact, and notify stakeholders, while AI-driven automation enriches lineage by tagging sensitive data, linking technical fields to business terms, and flagging potential quality issues. They also monitor pipelines for anomalies and unexpected changes, ensuring that data remains reliable and trustworthy across the entire data landscape.
Integration capabilities
The best solution integrates with the systems and applications your organization uses, so it can automatically and accurately map data lineage across your data landscape.
Business-friendly visualization
Data lineage diagrams that are easy to read by business users as well as technical users are a must-have feature because they offer clear visibility into the data flow, allowing all users to view and understand every step of the journey.
Data cataloging
The best data lineage tools are integrated with a data catalog, which enables you to dig into data from lineage diagrams to see more details, such as asset description, owner, business terms, data quality insights, and more.
Augmented data lineage
Augmented data lineage doesn’t just track technical flows, it enriches them with business context. Lineage that is enriched with data quality insights, business terms, and detected anomalies — all directly displayed in lineage diagrams — provides additional insights that enable you to better track data quality, monitor PII, and identify issues throughout the data lifecycle, so that you can keep your data reliable and secure.
Unified platform
Gone are the days when lineage tools were purchased as standalone solutions. Today, they are integrated into broader data trust and governance platforms, bringing everything together in one place.
Combining lineage with data quality, catalog, and observability capabilities is not only more convenient and cost-efficient, but it also streamlines audit trails and simplifies the troubleshooting of data quality issues by consolidating all the necessary information in a single platform.
Elevate your data lineage capabilities with Ataccama!
Data lineage is a necessity for organizations that want to better understand their data, identify and resolve issues quickly, and ensure data is always reliable and secure.
Ready to take the next step? Watch our data lineage webinar to see Ataccama’s data lineage software in action and discover how Ataccama can give you clear visibility, automation, and integration across your entire data environment.