Govern your data, unlock your potential
Ataccama ONE’s automated and integrated platform simplifies data governance. From data discovery to regulatory compliance, empower your team to make confident, data-driven decisions

Reduce costs, boost trust, and drive efficiency
Organizations worldwide trust Ataccama ONE to transform their data governance programs. Our platform delivers measurable results, helping you make data-driven decisions with confidence.

Transform your data into a trusted asset
From compliance to innovation, Ataccama ONE helps you govern, protect, and maximize the value of your data across your organization.




Simplify compliance with
automated governance tools
Ataccama ONE helps you protect sensitive data, manage consent, and implement policies to meet standards like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and others. Reduce the risk of fines and safeguard your reputation. 



Create personalized
customer journeys
Unify your customer data to understand individual preferences and behaviors. Ataccama ONE empowers you to deliver personalized interactions, targeted campaigns, and seamless omnichannel experiences that delight customers. 


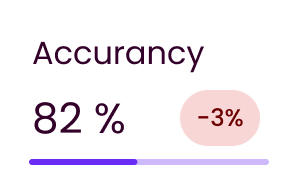
Streamline operations with
automated customer data
management
Eliminate manual data processes and reduce overhead with Ataccama ONE. Automate customer data integration, quality checks, and deduplication to improve efficiency and free up valuable resources. 

Improve AI/ML outcomes with
accurate customer data
High-quality customer data is essential for successful AI/ML initiatives. Ataccama ONE ensures your data is accurate, consistent, and ready to fuel your AI/ML models, leading to better predictions, personalized recommendations, and improved business outcomes. Ataccama ONE for data governance
Automate data quality, discovery, and classification with AI-driven tools. Build a trusted foundation for business innovation and compliance.
Data discovery and classification
Identify sensitive data, calculate quality metrics, and prioritize governance initiatives using Ataccama ONE’s integrated metadata and data processing capabilities.

Automated data quality
Effortlessly monitor, cleanse, and enrich data across all systems. Detect anomalies, flag issues, and maintain high-quality data for trusted insights.

Business glossary
Centralize business terms, hierarchies, and rules. Collaborate to define and automate their use for consistent understanding across teams.

Augmented data lineage
Automatically capture and visualize data lineage across systems, enriched with data quality insights to ensure trust and drive confident decisions.

What our customers say
Learn how T-Mobile streamlined PII protection with Ataccama


T‑Mobile thrives thanks to data‑at‑scale initiative
-
Challenge
The leading mobile and 5G carrier sought an enterprise-wide data transformation to secure its data, maintain regulatory compliance, save time and reduce costs, and, ultimately, accurately predict customer behavior and intention.
-
Solution
Implementing a centralized management solution, build a robust data quality solution - an enterprise-grade tool to scan large volumes of databases and quickly identify sensitive or PII data, curate a single source of truth for internal and external data.
-
Results
- $350 million in cost-avoidance and consumer protection by eliminating the risk of PII leakage
- $50 million in savings through data reuse and removing redundant systems and databases
- $25 million in savings by reducing data preparation times for AI teams.
Ataccama
features Learn more about our capabilities for data governance

See the platform in action
Get a personalized walkthrough from our experts to discover how Ataccama can help you.
Tailored for your industry
Learn how businesses in your industry are leveraging Ataccama for success.


















