Are you a data professional mandated to deliver a priority business initiative? Or maybe you’re a business leader responsible for one or more critical business processes heavily reliant on data. In either case, if poor quality, messy, and duplicated data is holding you back, you’re in the right place.
From building customer self-service apps to enhancing customer segmentation or offering highly adaptable predictive models that drive cross-sells, there are many situations where having up-to-date, consolidated data is a must. But is it critical to manage one type of data over others? That might be the case for companies with multiple sources and data domains. Read more and learn what Master Data Management is and how it can help.
What is master data?
Master data is a term that describes the most valuable business or operational data. It defines core business entities like customers, products, and suppliers, offering a consistent source of business data for accurate reporting and decision-making.
There are different types of domains for master data, and they are defined by their own set of attributes or unique characteristics. Here are some examples:
| Domain | Attributes |
| Customer | (Both B2B/B2C) First name; last name; address; postal code; buying preferences, Service-Level-Agreements |
| Product | Product code; color; size; design; storage (SKU) |
| Location | Addresses; type of location (e.g., consumer, warehouse, retail location); logistic coordinates (geocoding) |
Since it’s your most important data, managing your master records is essential to any data management initiative. The only problem worse than a data issue is a data issue with your most valuable data.
How master data management helps improve critical business processes
MDM has a broader mission that goes beyond governing master data and reference data. MDM’s ability to centrally merge and govern data from any enterprise system brings powerful business benefits in the areas of operational effectiveness, regulatory compliance, and customer segmentation.
Operational effectiveness
Maintaining a unified view of your master data can increase efficiency across many business operations. Enhancing data quality and consistency leads to fewer errors that can slow down processing and compromise service delivery. Implementing an MDM tool will streamline workflows, reduce IT overhead by automating data management processes, and increase straight-through processing rates (automated processes done purely through electronic transfers with no manual intervention involved). Finally, a single, accurate view of your master data will lead to faster decision-making, allowing you to adjust to market trends more flexibly.
Regulatory compliance
Regulatory compliance requires your company to follow the rules and regulations set up by governing authorities regarding the data you collect. MDM can help by improving data governance, enhancing data security, and maintaining accurate audit trails (should your company fall under a data audit). It also aids in optimizing reporting practices and makes it easier to manage customer consent changes. MDM functionalities like data anonymization are beneficial when maintaining compliance with regulations such as GDPR.
Customer segmentation
Customer segmentation involves dividing customers into smaller groups to apply marketing activations more precisely. MDM makes this easier by providing a singular customer view that keeps consistent data across all channels. Having a consolidated, up-to-date golden record of each customer allows organizations to move data easily from their main system to various environments. They can then enrich those records with more complex attributes from external sources and third-party applications. This significantly reduces the go-to-market time for client-facing campaigns and enables more reliable predictive analytics.
The negative effect of unmanaged master data
Like all data, master data needs to be managed to extract maximum value. Redundant master data is confusing, and you are likely to find duplicates of multiple records, even within a single system application or database. For example, a customer record may exist where the names match, but the addresses do not, or the addresses are stored in different formats.
Here’s an example of how missing data, inconsistencies in format, and misspellings can lead to siloed systems creating their unique versions of the same customer:
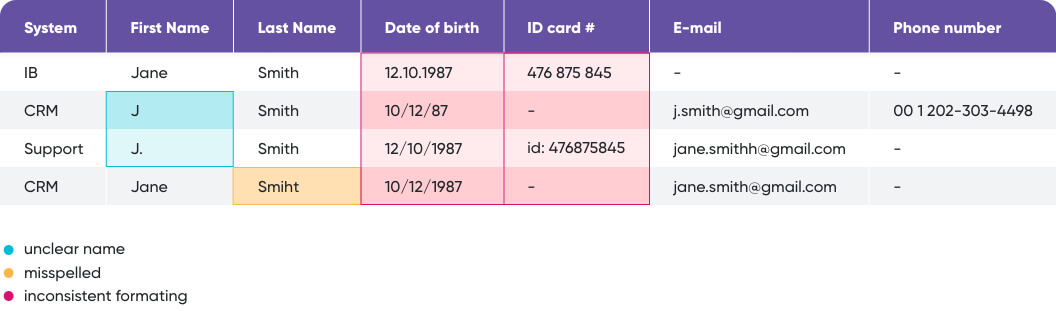
Four records of Jane Smith exist in three systems. From a human perspective, we can judge there’s probably only one customer named Jane Smith, born on October 12, 1987.
Or could the other record in the CRM system represent a John Smith, born on December 10, 1987? We can’t be sure because one of the records has just one letter for the first name, the other record is missing the phone number, both are missing an ID card number, and their emails don’t match. This could still be Jane Smith with a new email address.
From a business perspective, this classic and systemic data management problem can seriously impact a customer’s relationship with your company, creating:
- Inaccurate sales reports about Jane Smith, whose customer record is duplicated in different systems.
- Inadequate customer service provided to Jane Smith because support agents might have wrong and incomplete contact and product information.
- Increased marketing costs when sales materials are repeatedly and mistakenly sent to Jane Smith.
- Missed opportunities to upsell to Jane Smith because her buying history is siloed and not linked to her customer record.
- Unnecessary reputational damage that comes as a result of all the previous actions not being addressed in a timely manner.
The most common examples of master data management
Now that we know what MDM is and how it helps, let’s cover some of the types available to companies.
Customer master data management
Customer MDM helps with the processes companies use to maintain customer data across various systems and databases. It typically includes key customer data points such as name, address, contact information, transaction history, etc. One of the main goals of customer MDM is to generate a 360-degree view of the customers and a comprehensive, unified view of every customer profile.
Vendor/Supplier master data management
Vendor MDM creates a golden record for a company’s vendors and the people who sell their products. It can contain information like names, addresses, contact persons, payment terms, tax identification numbers, etc.
Product master data management
Product master data refers to the critical information a company collects about its products. It can contain items like inventory management, sales, marketing, procurement, and supply chain operations.
Conclusion
MDM is for you if you’re in an organization with multiple lines of business, with overlapping customers, products, or suppliers. You depend on large volumes of high-quality data spread across multiple systems to run your operations. It is the go-to data management solution for creating a single version of the truth from numerous conflicting datasets and systems.
To summarize, MDM provides its value through its ability to
- Create and maintain the best version of business information.
- Connect data from different domains into valuable business views.
- Make key business data accessible to users, systems, and processes securely and governed.
Ultimately, this means organizations can use reliable data for a wide range of tactical activities and ongoing core business processes.
Want to take the next step in your MDM journey? If you're struggling with duplicate or low-quality customer data, this article on Customer Master Data Management is for you.
Read more about: The urgency of consolidating customer data with MDM
Find out how Ataccama ONE MDM can help
Put and end to duplicate data and siloed systems. Start consolidating critical data automatically and provide a single source of truth across your organization.
Visit our MDM Product Page