Governments' standards and policies that protect individuals' data are growing stronger. We've already seen the sweeping changes from the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act. New changes are also coming to the APAC region with Australia's Privacy Bill introduced in October 2022.
Regardless of your region's policies, one conclusion is universal: it's cheaper to remain compliant than to interfere with regulations. While the average cost of compliance is about $5.5 million (for an intermediate-sized organization), the risks of noncompliance can run almost as high as $15 million:
- Business disruption: $5.1 Million
- Productivity l oss: $3.8 Million
- Revenue loss: $4 Million
- Fines, penalties, & other: $2 Million
Implementing an advanced data stack can help you avoid these hefty fines by automating your data's protection and keeping it compliant with the latest rules and regulations. Here are some of the data management tools you need to keep your company compliant:
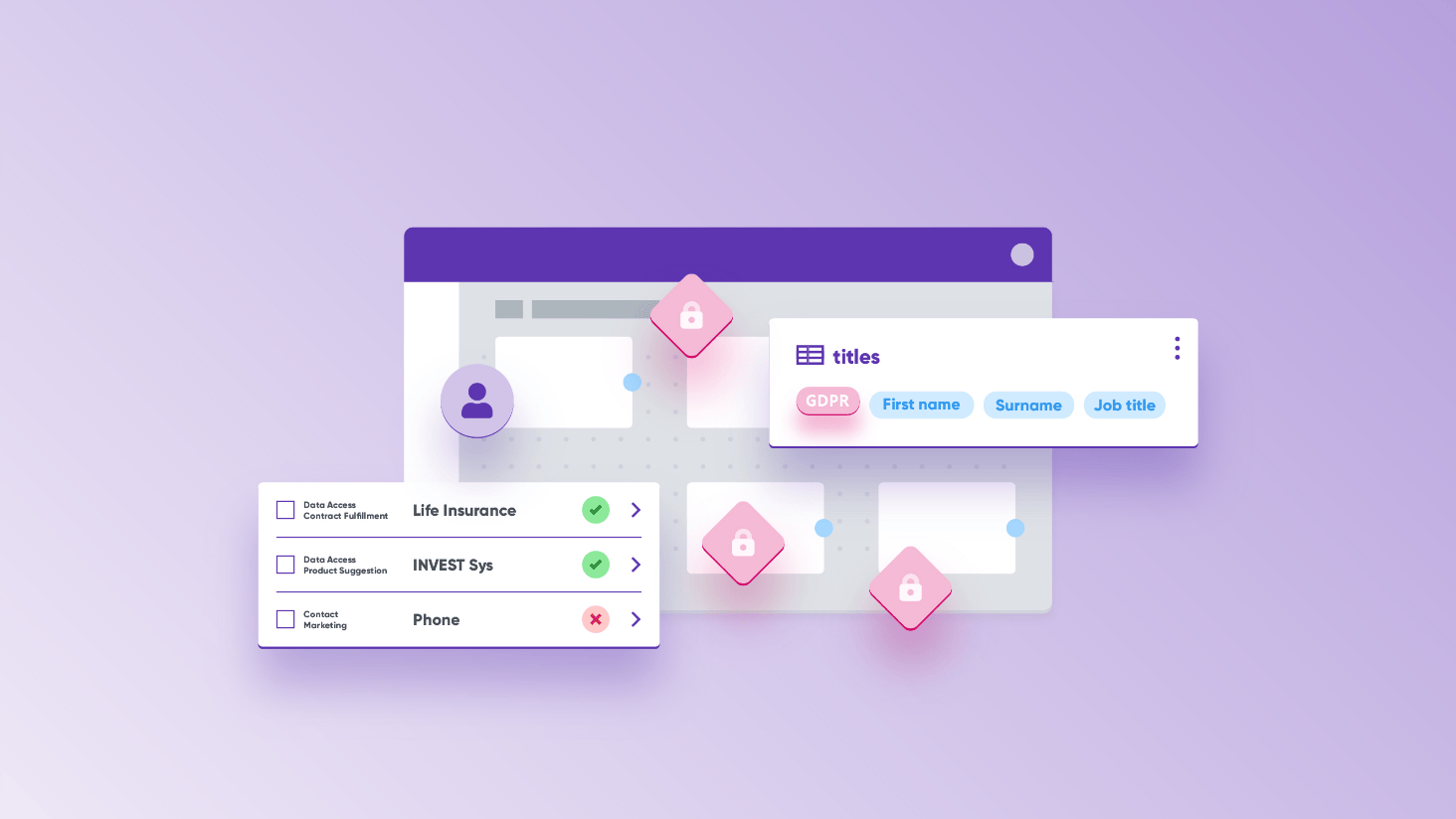
Automated Data Catalog
An automated data catalog - i.e., a catalog that automatically discovers your data sources and the quality of data within them - is where you will create an inventory of and organize all your company’s data assets to make them readily available for further use. However, enabling the use of data mustn’t interfere with policies and standards mandated by the state. Some of the main features of your data catalog that will help you remain compliant are data classification, lineage, data observability, and policy management.
Let's understand how each feature relates to worldwide data rights and protection policies.
Data classification
Data classification is the process of organizing data by labeling and tagging it into categories. This is an important enabler of data security and protection as ordered by government regulations. Most of these policies (like the GDPR in the EU and Privacy Act in Australia) mandate making your sensitive and personally identifiable information (PII) data readily available - to both government agencies and the individuals (who are the subject of the data) upon their request.
Data classification allows you to identify and categorize the data into groups based on common characteristics, like being deemed "critical" under these regulations. As such, it will become easier for your organization to understand what types of data you are processing and storing. Also, your company’s data will become easily searchable and trackable, speeding up the time it takes to securely access relevant data, limiting those who have access to it, and closely monitoring how it is used/manipulated during storage in your systems.
Data classification should be conducted continuously to meet data privacy compliance requirements. To enable this continuous monitoring of all your systems, a data catalog should offer automation features that will benefit you in the following ways:
- It will enable you to build and maintain a knowledge base of your data landscape by connecting to (and automatically and regularly scanning) all your data sources.
- It will enable faster classification by using AI-based classification rules and business terms suggestions.
Here is how to get started with data classification:
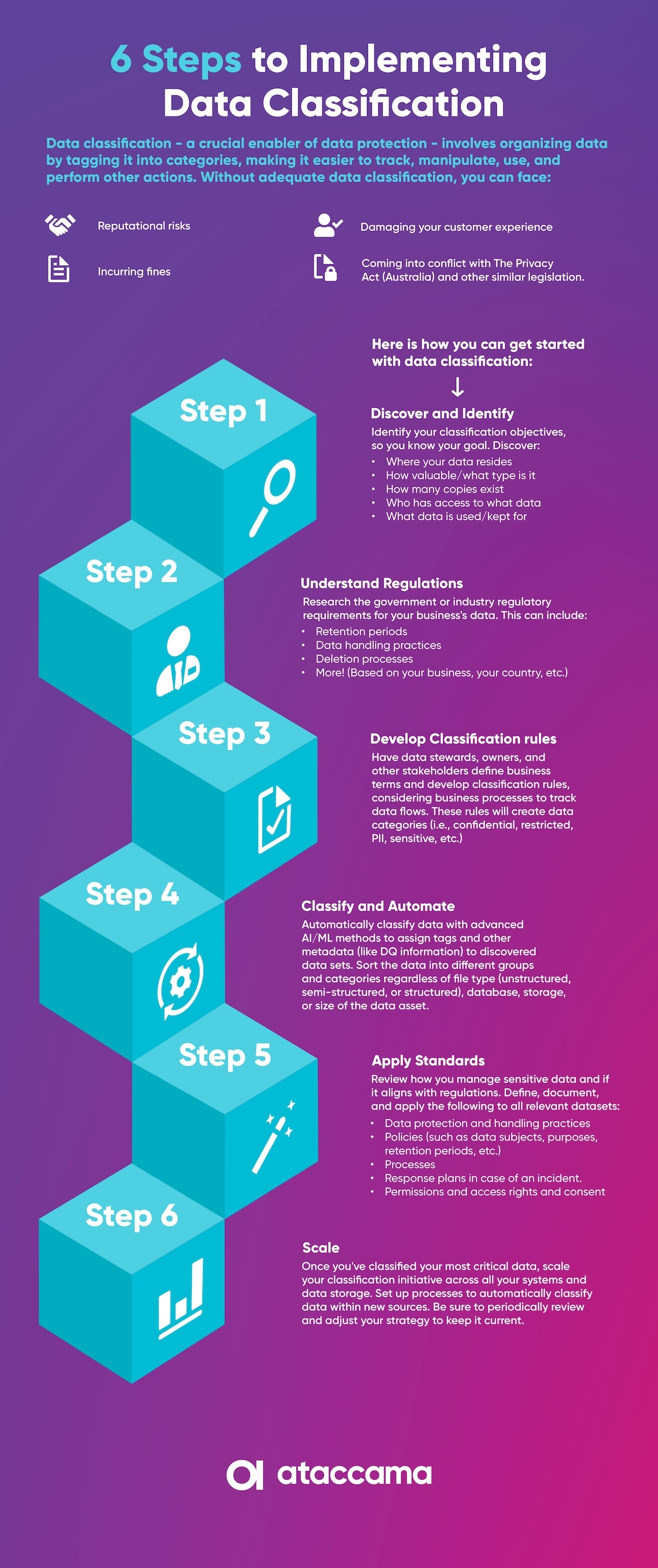
For example, the GDPR defines sensitive data as: "special categories of personal data," including race, ethnicity, political opinions, religious or philosophical beliefs, genetic data, health data, information concerning someone's sex life, and much more. If you have any data of this nature stored in your system, you could label it as "sensitive data" and monitor its access, retention time, and anything else you would need to stay compliant.
Lineage
Data lineage tracks your data’s journey from its source to its eventual end purpose. It logs every step along the way, explaining how and why the data was moved from one location to the next.
In terms of compliance, lineage will help you track and prevent data breaches by tracking data flows and spotting issues when and where they happen in your data pipeline so that you can resolve them and put preventative measures in place. It can also help with the data documentation process by giving you precise information about applications and data, and thus help with the due diligence efforts for data compliance. You can follow the pipeline to find the leakage as data flows through systems, identify if you have any sensitive data in legacy systems (or just in general), and expose the existence of unknown sources of data.
You can also analyze who has access to each system and remain transparent with regulatory authorities about who had access to the data, where it was stored, and how long you kept it before, after, and during the breach. This will help prevent future breaches because you can assess your weak points and improve upon them so you don't repeat your mistakes.
For example, the GDPR mandates that organizations demonstrate "accountability" for their data. This includes maintaining a record of processing activities. Data lineage provides an auditable trail of data processing activities, allowing companies to demonstrate compliance at every stage of the data lifecycle, from the source to its eventual use in the organization.
Observability
Data observability is an automated process that uses AI-enabled data management technologies to monitor the overall health of your company's data. It allows you to detect, troubleshoot, and alert data owners about unexpected changes in data or other problems that occur along the data pipeline in real time.
This can help with compliance standards in two ways: maintaining high data quality and enabling an understanding of your stored data.</ p> Maintaining high data quality
Many of these regulations mandate a certain standard for data quality. The GDPR upholds that personal data must be accurate, up-to-date, and relevant for its initially intended purpose. Observability can help you manage data quality at scale and across all your systems by enabling easy and bulk monitoring configuration. As a result, data owners will be notified about data quality drops, or schema and volume changes.
In addition, one of the features of data observability is also anomaly detection. This scans for patterns in your data to notice when unusual changes occur. If this feature detects an anomaly in your PII data, it could alert you immediately, allowing you to respond and fix the problem before any of the data is negatively impacted or falls below the quality standards of the GDPR.
Enabling understanding
The second way data observability relates to compliance standards is by enabling an understanding of what data is stored in which business systems. It allows you to schedule regular systems scans to uncover existing or new data and easily add new systems when needed. Such automation can save your staff countless hours on manual maintenance of your systems, as well as issue mitigation.
Policy Management
The policy management capability of the data catalog can turn government policies into company policies while balancing the boundaries for data usage with effective strategies to reach business objectives. It's a central place where you can describe and document your data governance: i.e., data rules related to usage, access, security, and established processes. It can serve as a central location for collecting principles, frameworks, programs, roles, and responsibilities related to data management.
The policies that live here will be a reference for the overall handling of data at your organization. Business and technical users can use them when working with data or creating data quality rules, ensuring they (and your data systems) stay in line with government regulations. This will increase transparency for data handling necessary for your business users and auditors.
You can use the policy management capability to define rules such as: who should be responsible in case of a data breach, which government bodies need to be notified (and how/when), who can have access to sensitive data, what data is considered "sensitive," etc.
Any organization storing and processing sensitive data must have relevant governance policies. Universities with multiple policies - defining the scope and purpose, principles, roles, and responsibilities - are a great example of what such policies should look like and contain. In addition, as a best practice, companies managing large amounts of data should have multiple policies in place to account for various categories of data.
Master data management
Master data management (MDM) involves the creation of a singular record of an organization's master data (the most critical data to an organization, i.e., customer, product, and employee data). This process ensures that no duplicate data exists and that incomplete records can be enriched from external systems and services.
Employing a solution like this can help with compliance in three ways:
- Keeping an exact record of all your sensitive data. By managing your most sensitive data as master records, you can ensure it remains compliant and know exactly where everything is stored. Not only will you be able to access it more efficiently, but it will also make it easier to monitor and limit who is accessing this data, aligning the access rights with the level of data sensitivity at hand. Regardless of who needs access to the data, whether it's regulatory entities or individuals exercising their rights, having these capabilities will make it possible to find and provide it as soon as possible.
- Ensuring that all of your stored sensitive data is protected. Keeping a master record of your most sensitive data makes it easier to implement additional measures to ensure it is secure. It will also be easier to track what data needs to be protected, as it will automatically be added to the MDM hub.
- Manage consents. An MDM solution can (and should) also consolidate consent in the master record. That means that your approved consent to collect, store, and use customers' data would be available in the same place as your customer data, ensuring visibility on what the master consent is and how all of the existing data complies with it. You'll also be able to identify source systems affected by the same consents. Finally, you can consolidate consent at different levels (so if a customer approved consent at one level but refused it at another, you'll know where/how you can or cannot use their data).
For example, If an individual requests the deletion of their data, the MDM could find all the sources where that customer's data is stored and erase them. If possible, it can delete that data from the source systems directly. Otherwise, you can contact the system owners and create an aggregated list of the records that need to be deleted. Then logically delete the master record and monitor for a while to see if any source systems try to deliver you another copy of the affected record, revealing that the source system didn't completely delete the record to begin with.
Let Ataccama help you remain compliant
All the tools mentioned above are a part of the Ataccama ONE platform that unifies Data Governance, Data Quality, and Master Data Management into a single, AI-powered solution regardless of your specific use case and data sources. The Ataccama ONE platform allows your business and data teams to innovate with unprecedented speed while maintaining trust, security, and data governance.